Unlocking Workforce Potential: A Deep Dive into HR Business Intelligence Software Applications
In today’s dynamic business landscape, data is the new currency. Companies are constantly seeking ways to leverage information to gain a competitive edge. Human Resources (HR) departments are no exception. They are increasingly turning to HR Business Intelligence (BI) software applications to transform raw data into actionable insights. This article provides a comprehensive overview of HR Business Intelligence software applications, their benefits, and how organizations can effectively implement them.
The Rise of Data-Driven HR
Traditional HR processes often relied on intuition and anecdotal evidence. Decisions were frequently made without a complete understanding of the workforce. This is changing rapidly. The shift towards data-driven HR is fueled by several factors. These include the increasing availability of data, the need for greater efficiency, and the desire to improve employee engagement and retention. HR Business Intelligence software applications are at the forefront of this transformation.
HR Business Intelligence software applications enable HR professionals to collect, analyze, and interpret data related to employees. This information can then be used to make informed decisions about hiring, training, compensation, and performance management. The goal is to move beyond reactive HR and adopt a proactive, strategic approach. This approach directly contributes to organizational success.
Understanding HR Business Intelligence Software Applications
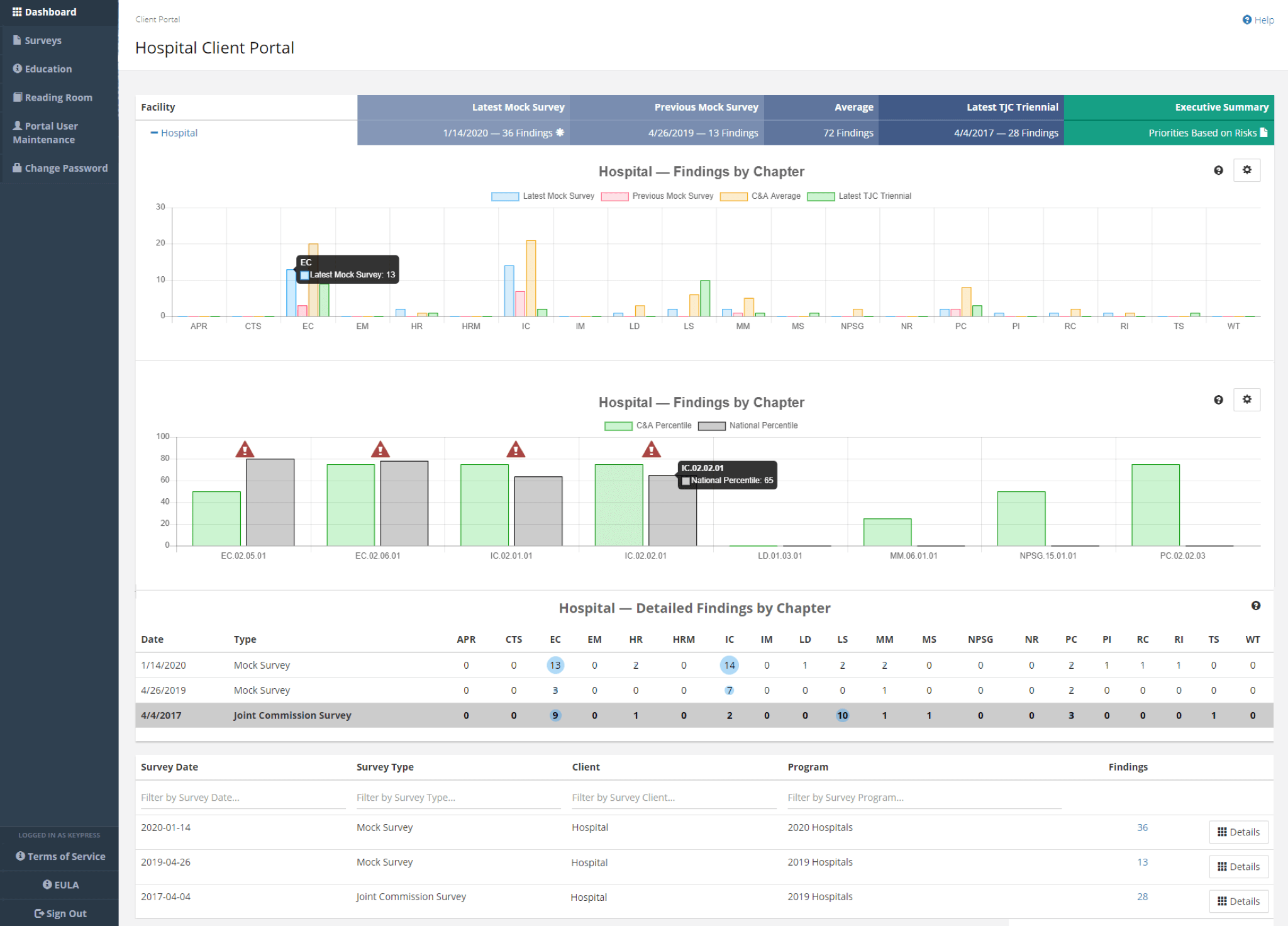
HR Business Intelligence software applications are designed to provide insights into various HR-related areas. These include workforce demographics, employee performance, recruitment effectiveness, and compensation analysis. The software typically integrates with existing HR systems, such as Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS) and Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS). This integration ensures data accuracy and completeness.
The core functionality of HR Business Intelligence software applications often includes:
- Data Collection: Gathering data from various sources, including HRMS, payroll systems, and performance management tools.
- Data Warehousing: Storing and organizing data in a central repository for easy access and analysis.
- Data Analysis: Using various analytical techniques, such as statistical modeling and trend analysis, to identify patterns and insights.
- Reporting and Visualization: Generating reports and dashboards that present data in a clear and concise format.
- Predictive Analytics: Using historical data to forecast future trends and make proactive decisions.
These features empower HR professionals to make data-driven decisions. They can improve HR processes and contribute to overall business goals.
Key Benefits of Implementing HR Business Intelligence Software Applications
Implementing HR Business Intelligence software applications offers numerous benefits to organizations. These benefits can lead to significant improvements in HR efficiency and effectiveness. Some of the primary advantages include:
- Improved Decision-Making: Data-driven insights help HR professionals make more informed decisions about talent acquisition, compensation, and employee development.
- Enhanced Workforce Planning: By analyzing workforce demographics and trends, organizations can better plan for future staffing needs.
- Increased Efficiency: Automation of reporting and analysis tasks frees up HR staff to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Reduced Costs: Identifying and addressing inefficiencies in HR processes can lead to significant cost savings.
- Improved Employee Retention: Understanding employee needs and preferences allows organizations to create a more engaging work environment.
- Better Talent Acquisition: Analyzing recruitment data can help organizations identify the most effective sourcing channels and improve the quality of hires.
- Enhanced Compliance: HR Business Intelligence software applications can help organizations ensure compliance with employment laws and regulations.
These advantages collectively contribute to a more strategic and effective HR function. They help organizations achieve their business goals.
Core Features to Look for in HR Business Intelligence Software
Selecting the right HR Business Intelligence software application is crucial for success. Organizations should consider several key features when evaluating different options. These features ensure the software meets their specific needs.
- Data Integration: The ability to seamlessly integrate with existing HR systems, such as HRMS and ATS.
- Data Visualization: User-friendly dashboards and reports that present data in a clear and concise format.
- Advanced Analytics: Capabilities for performing statistical analysis, trend analysis, and predictive modeling.
- Customization: The flexibility to customize reports and dashboards to meet specific business needs.
- Security: Robust security features to protect sensitive employee data.
- Scalability: The ability to handle increasing amounts of data as the organization grows.
- User-Friendliness: An intuitive interface that is easy for HR professionals to use.
- Mobile Access: The ability to access reports and dashboards on mobile devices.
Prioritizing these features allows organizations to choose the best software solution. This ensures they can effectively leverage data for HR decision-making.
Implementing HR Business Intelligence Software: A Step-by-Step Guide
Implementing HR Business Intelligence software applications requires a systematic approach. Following a structured implementation plan can help ensure a successful deployment. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Define Objectives: Clearly define the goals and objectives of the HR BI initiative. What specific problems are you trying to solve?
- Assess Needs: Evaluate the organization’s current HR data landscape and identify data sources. Determine what data is needed for analysis.
- Select Software: Choose the HR Business Intelligence software application that best meets your needs and budget. Consider the features mentioned earlier.
- Data Integration: Integrate the software with existing HR systems and data sources. Ensure data accuracy and consistency.
- Data Cleansing: Clean and validate the data to ensure its quality. Remove any inconsistencies or errors.
- Develop Reports and Dashboards: Create reports and dashboards that provide actionable insights. Tailor them to the needs of different users.
- Train Users: Provide training to HR staff on how to use the software and interpret the data.
- Monitor and Evaluate: Regularly monitor the performance of the software and make adjustments as needed. Evaluate the impact of the initiative and measure its success.
- Iterate and Improve: Continuously refine the use of the software and explore new ways to leverage data for HR decision-making.
Following these steps can help organizations successfully implement HR Business Intelligence software applications.
Real-World Applications of HR Business Intelligence
HR Business Intelligence software applications are used in various ways across different industries. They provide valuable insights that drive decision-making. Several examples showcase the practical applications of this technology:
- Talent Acquisition: Identifying the most effective recruitment channels. Analyzing the time-to-hire and cost-per-hire. Improving the quality of hires.
- Employee Retention: Identifying factors that contribute to employee turnover. Predicting which employees are at risk of leaving. Implementing targeted retention strategies.
- Performance Management: Tracking employee performance against goals. Identifying high-performing employees. Providing feedback and coaching.
- Compensation Analysis: Analyzing compensation data to ensure fair and competitive pay. Identifying pay gaps. Making informed decisions about salary increases.
- Training and Development: Identifying skill gaps. Assessing the effectiveness of training programs. Personalizing training opportunities.
- Workforce Planning: Forecasting future staffing needs. Analyzing workforce demographics and trends. Optimizing workforce allocation.
These examples demonstrate the versatility of HR Business Intelligence software applications. They can be used to address a wide range of HR challenges and opportunities.
The Future of HR Business Intelligence
The field of HR Business Intelligence is constantly evolving. New technologies and trends are emerging. These will shape the future of HR analytics. Several key developments are worth noting:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI and machine learning are being used to automate data analysis. They are also being used to provide more sophisticated insights.
- Predictive Analytics: Predictive analytics will become even more sophisticated. They can forecast future trends and outcomes.
- Big Data: Organizations will continue to collect and analyze increasing amounts of data. This data includes data from social media and other external sources.
- Data Visualization: Data visualization tools will become more interactive and user-friendly. They can help users understand complex data more easily.
- Employee Self-Service: Employees will have greater access to HR data and analytics. This will empower them to make informed decisions about their careers.
These trends will transform how HR departments operate. They will enhance their ability to support organizational goals.
Challenges and Considerations
While HR Business Intelligence software applications offer significant benefits, some challenges exist. Organizations need to address these challenges to ensure a successful implementation. Some key considerations include:
- Data Quality: The accuracy and completeness of data are critical. Poor data quality can lead to inaccurate insights and flawed decisions.
- Data Security and Privacy: Protecting sensitive employee data is essential. Organizations must implement robust security measures.
- User Adoption: Ensuring that HR staff are trained and comfortable using the software. This is important for maximizing its value.
- Integration Challenges: Integrating the software with existing HR systems can be complex. Careful planning and execution are essential.
- Cost: The cost of HR Business Intelligence software applications can vary. Organizations must consider their budget and return on investment.
Addressing these challenges can help organizations maximize the value of their HR Business Intelligence software applications.
Conclusion
HR Business Intelligence software applications are becoming increasingly essential for modern HR departments. They empower organizations to make data-driven decisions. These decisions improve workforce management and drive business success. By carefully selecting and implementing the right software, organizations can unlock the full potential of their workforce. They can also gain a significant competitive advantage. The future of HR is data-driven, and HR Business Intelligence software applications are at the forefront of this transformation.
[See also: Best Practices for Data-Driven HR]
[See also: How to Choose the Right HR Software]
[See also: Leveraging HR Analytics for Business Growth]